HYDROELECTRICITY

History
The power of water has been used in ancient civilizations since the 4th century BC in the form of waterwheels and watermills. The way to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels is to increase renewable energy production opportunities since we cannot survive without energy. Free energy is a necessary commodity if we must face next ice age or mini-ice age comfortably. Among all renewable energy sources, hydroelectricity is the most economical and reliable energy source. Hydroelectricity, which produces electricity from the energy of flowing, moving, or falling water, has significant potential as a renewable energy source.
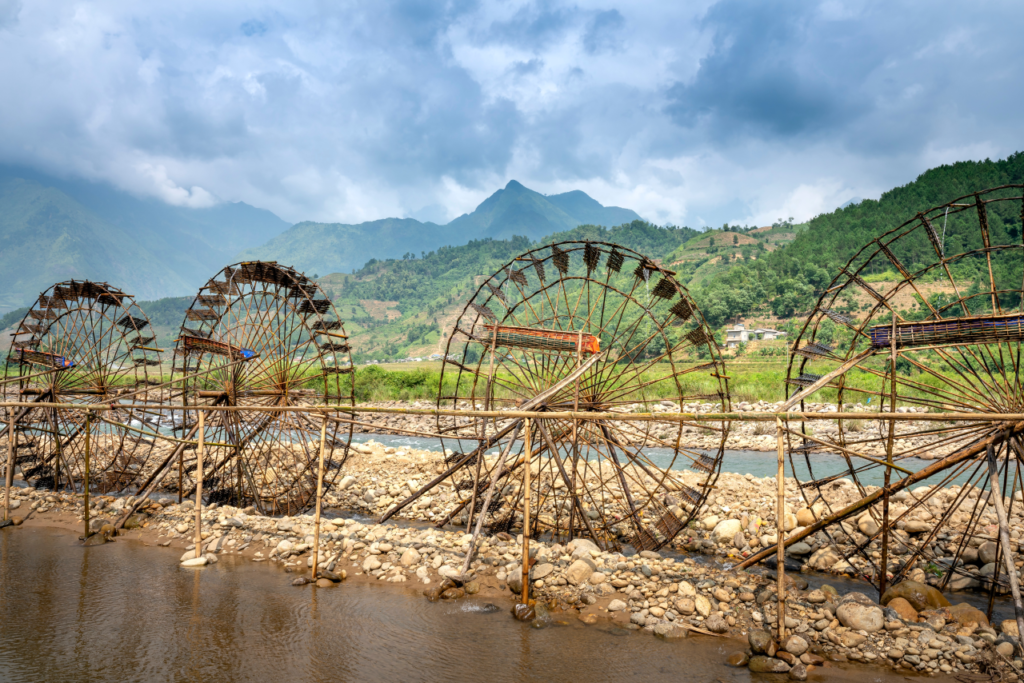

Hydropower has been used to generate electricity for over 100 years. The first advocate and first user of hydropower was Lord Armstrong. In 1870 he used the lake’s hydroelectric power to electrify his home in Crag side. Hydroelectricity is considered as a renewable energy source because the water that drives the turbines is continuously replenished by precipitation and snowmelt. It is also an environmentally friendly energy source as it does not emit greenhouse gases or other pollutants during operation. Hydroelectricity is a reliable and relatively inexpensive source of energy because the energy source is free and abundant.
Hydroelectric power is typically created by constructing a dam across a river or other body of water to form a reservoir. The power of the water flowing through the dam’s turbines generates electricity that can be distributed through the electrical grid to homes, businesses, and other consumers. Many countries use rivers for hydropower by building hydroelectric power plants and dams across them. Some countries are almost entirely dependent on hydropower for their energy needs, as most of their electricity needs are met by hydropower. Most of the earlier hydroelectric power generation on the river is related to the construction of large-scale dams and hydroelectric power plants. These big dams change the ecology of the area in which they are built.
Here are some key aspects of potential of hydroelectric power:
- Largest Renewable Energy Source: Hydroelectric power plants is currently the largest source of renewable electricity globally. It accounts for a significant portion of the world’s renewable energy generation, contributing to electricity grids and meeting growing energy demands. As per Wikipedia 2019 world hydroelectric power generation was 27petawatt hours 16% of the total electricity generation.
- High Energy Density: Hydroelectric power plants can generate a large amount of electricity from a relatively small amount of water. The energy density of flowing or falling water is much higher compared to other renewable resources such as wind and solar power, allowing hydroelectric power plants to generate significant power.
- Reliable and Manageable: Hydroelectric power plants provides a reliable and manageable source of electricity. It can be configured to provide base load power to meet constant power demand or to meet peak demand. By regulating the flow of water through the reservoir, Hydroelectric power plants can respond quickly to fluctuations in electricity demand.
- Long Life: Hydroelectric power plants typically have a lifetime of several decades. With proper maintenance and operation, these plants can provide continuous electricity generation over extended periods, contributing to long-term energy stability and security.
- Water Storage and Flood Control: Hydropower reservoirs can serve as water storage systems, helping manage water resources and supply during dry periods or droughts. Additionally, they can assist in flood control by regulating water flow and mitigating the risk of downstream flooding.
- Emission Reduction Potential: Hydroelectric power is a clean energy source that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions during operation. By displacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation, it contributes to reducing carbon dioxide and other air pollutant emissions, mitigating climate change, and improving air quality.
- Multi-Purpose Benefits: In addition to electricity generation, hydroelectric power plants often offer additional benefits such as water supply for irrigation, recreation, and navigation. These multi-purpose projects can provide multiple services, enhancing the economic and social value of hydroelectric power plant investments.
It’s important to note that while hydroelectric power plants offer many advantages, there are also considerations related to environmental impact, including potential disruption to ecosystems, aquatic habitats, and downstream water availability. However, the construction of dams and reservoirs can have significant environmental impacts, including the displacement of communities and wildlife, changes to river ecosystems, impacting fish populations and the potential for flooding and landslides. There are also concerns about the effects of climate change on hydroelectric power generation, as changes in precipitation patterns and water availability could impact the amount of energy that can be generated. Three Gorges dam in China is the largest hydroelectric power station in the world currently. Filling up the dam’s reservoir has displaced many Chinese citizens. Sustainable planning and management practices are critical to minimizing these impacts and ensuring the responsible development of hydroelectric power projects. In addition, hydroelectric power generation is possible only in areas with sufficient water resources and topography suitable for dam construction.
The Department of Energy categorizes hydroelectric power plants into Micro, Small, and Large hydroelectric power plants according to their size. Large hydroelectric power plants include facilities exceeding 30 Megawatts. Small hydroelectric power plants can generate from 100 Kilowatts (kW) to 10 Megawatts. The capacity of the micro hydroelectric power plants is 100 Kilowatts (kW). Large hydroelectric plants can be used to power utilities, while smaller hydroelectric plants can be used to power homes, managed communities, or towns.
Small hydroelectric power plants are also classified as Mini hydroelectric power plants, Micro hydroelectric power plants and Pico hydroelectric power plants. Mini-hydroelectric power plants, also known as small-hydro plants, are a type of hydroelectric power plant that generates electricity from the movement of flowing water. They typically have a generating capacity of 100 Kilowatts to 10 megawatts. Mini hydroelectric power plants use Run of the river, impoundment, and diversion systems to produce electricity. Micro hydroelectric power plants use pumped storage, impoundment, and diversion systems to produce electricity. Pico hydroelectric power plants produce few watts to hundred watts. Run of the river, and impoundment, are used by Pico hydroelectric power plants to produce electricity use. Mini hydroelectric power plants can be useful to power homes, businesses, remote or off-grid locations and communities. Powering individual homes, small communities, and buildings in remote locations can be achieved using Micro hydroelectric power plants. Pico hydroelectric power plants may be useful power a single home, a small community, or even a small business.
Different turbines like impulse turbines, reaction turbines and cross flow turbines are used to convert the energy of the water. Archimedes Screw Generators, Cochlea Water Wheels, and Overshot Water Wheels also used in the conversion of energy of the flow of water
HYDROELECTRIC Power plants: SMALL
| Advantages | Advantages | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mini | Micro | Pico |
| Clean and renewable: Mini-hydro plants do not emit any greenhouse gases or other pollutants. | Micro hydroelectric power plants can be a valuable source of renewable energy. | Clean and renewable: Pico-hydro plants do not emit any greenhouse gases or other pollutants. |
| Sustainable: Mini-hydro plants can operate for decades with minimal maintenance. | They are relatively small and can be installed in a variety of locations, including rural areas. | Sustainable: Pico-hydro plants can operate for decades with minimal maintenance. |
| Reliable: Mini-hydro plants are a reliable source of electricity, even in areas with limited grid access. | Micro-hydro plants are also relatively clean and efficient, and they have a low environmental impact. | Reliable: Pico-hydro plants are a reliable source of electricity, even in areas with limited grid access. |
| Cost-effective: Mini-hydro plants can be relatively inexpensive to build and operate | They are a clean, renewable, and efficient source of energy that can help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. | Cost-effective: Pico-hydro plants are relatively inexpensive to build and operate. |
| Low environmental impact: Mini-hydro plants have a very low environmental impact compared to other types of power generation. | Community development: Pico-hydro plants can help to improve the lives of people in rural and remote communities by providing them with access to electricity. |
New versions of the Micro-hydroelectric power plants, Mini-hydroelectric power plants and Pico-hydroelectric power plants can help generate electricity from running water in rivers with little or no change to local ecosystems. Small hydroelectric power plants do not have any potential for big damage on failure like, Banqiao Dam, 1975.These power plants could be useful for generating energy from rivers with probably additional zero-carbon footprint. Micro-hydro and Pico-hydro are useful for generating electricity from flowing water, even small rivers and streams, as large rivers are not required to generate electricity from flowing water. There are rivers all over the planet. Every continent has rivers. There are thousands of miles of rivers available for Micro-hydroelectric power plants, Mini-hydroelectric power plants and Pico-hydroelectric power plants. Overall, hydroelectric power plants have significant potential to meet a large part of global energy demand, decarbonize electricity production and promote sustainable development.
Hydroelectric power plant uses the energy of running water to produce electricity. In 2019 as per Wikipedia, it was an important source of renewable energy, with 16% of the world’s electricity supplied by large-scale hydroelectric power plants. Further potential lies in the development of Mini, Micro or Pico. Hydroelectric power plant projects that can harness the energy of rivers and streams.
Although there are several countries in the world where hydroelectric power meets a significant portion of their energy needs, none currently fully meets their energy needs solely from hydropower. Some countries that generate most of their electricity from hydropower include Norway, Hydropower accounts for more than 96% of Norway’s electricity generation. Hydroelectric and geothermal energy supplies nearly 100% of Iceland’s electricity. More than 98% of Costa Rica’s electricity is generated from renewable sources, with hydroelectric power making up the largest share. Approximately two-thirds of Brazil’s electricity comes from hydropower. Hydroelectric power is the primary source of electricity in many Canadian provinces, accounting for approximately 60% of the country’s electricity generation. Top producers of hydroelectricity in the world in 2020 as per Wikipedia are China, Brazil, Canada, United States, Russia, India, Norway, Japan, Vietnam, and France. Table below show the countries and their percentages of hydroelectric power generation worldwide, along with what percentage of their domestic electricity needs met by hydroelectricity.
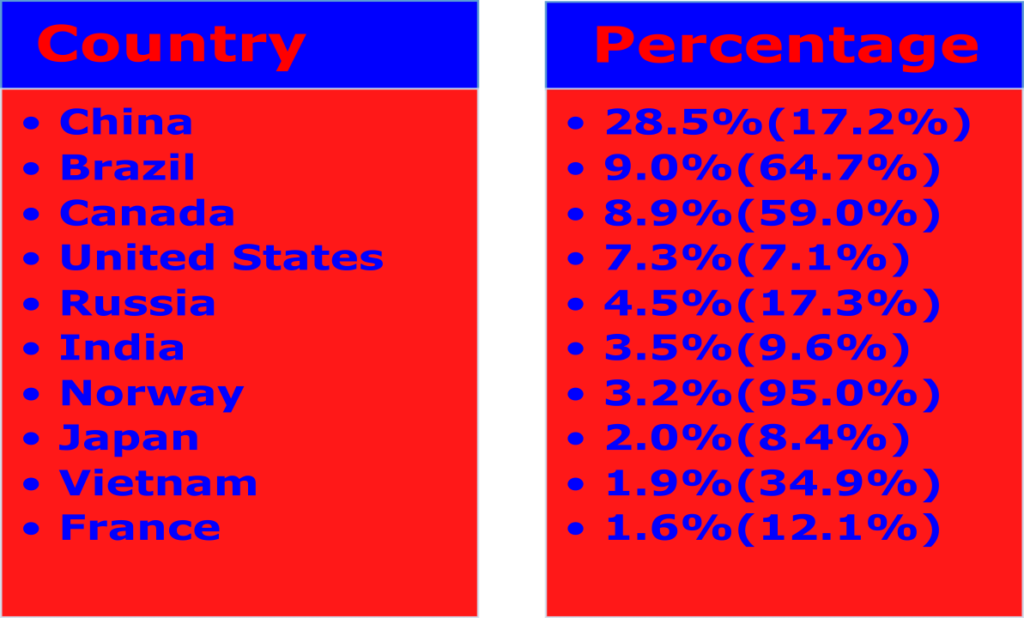
It is worth noting that even in countries with a high percentage of hydroelectric power generation, other sources of energy are often still required to meet their energy needs fully.
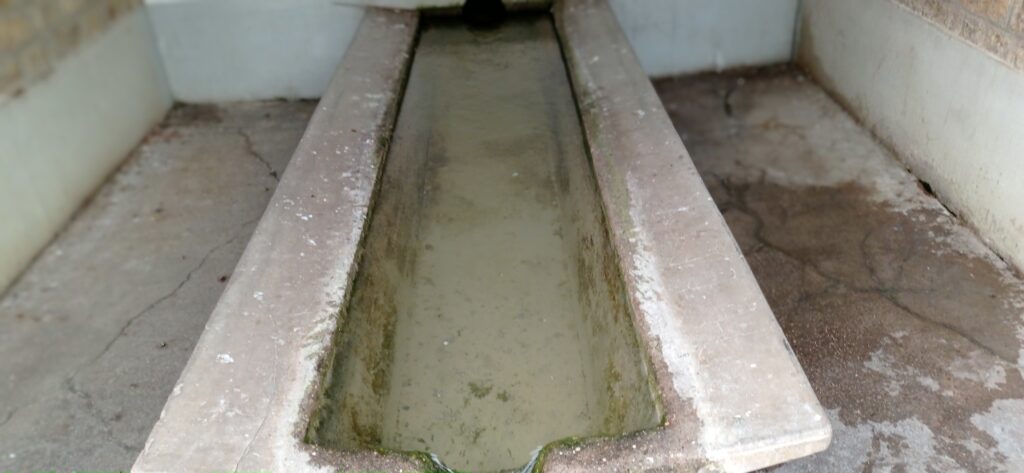

The above picture shows the construction from the past. The water collected from the mountains or hills nearby was used by people in the village to meet their water needs. Today it is abandoned.
It follows through the village for almost three kilometers and joins the river. In the last decade this stream taken out almost two to three meters of the banks depending on where you measure the banks. This ongoing soil erosion can endanger the houses on the banks as well as a bridge across the stream in the long run.
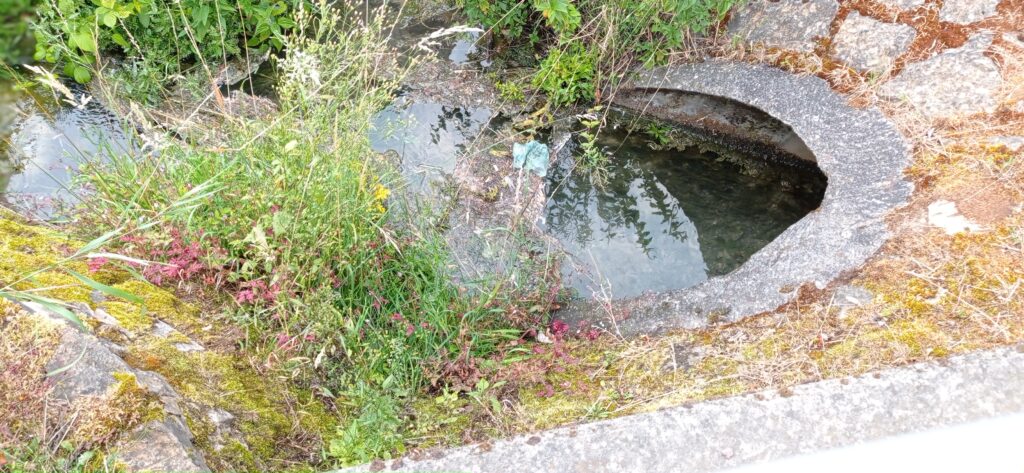

On the other hand, if the bank of this stream is fortified and put enough Micro or Pico hydroelectric power stations, it can probably power the small village with green or renewable energy through which it flows. This will also protect the banks from continued erosion. So local population can meet their energy needs through renewable green energy and at the same time reinforce the riverbanks through proper actions. If the local population share the cost of construction of the Micro or Pico hydroelectric power plants through a shareholder company, they can probably construct them without local government meeting the cost. In return shareholders as consumers of the power, can reduce their own energy costs. Unexploited rivers and streams can be considered as entrepreneur opportunities. Some countries the laws of electricity generation may be under government authority, so please consult local laws regarding these kinds of projects and startups.

If we make full use of the rivers and streams to generate electricity, then we have enough underexploited rivers and streams across the globe to probably meet a good percentage of our electricity needs through hydroelectricity production. Moreover, if we use Micro or Pico power plants to generate electricity then we may not cause too much damage to the environment or the ecosystems near the rivers. We will only using a renewable resource which produces green energy without any pollutants.
There are a lot of built-up rivers for cargo ships all around the world. Developing Mini, Micro or Pico power plants, to take advantage of energy of the flow of water especially in the built-up areas of the rivers can bring down energy prices in the countries with a lot of built-up river kilometers. Probably engineers and researchers from multidisciplinary fields can develop better hydroelectric power generators to take maximum advantage of the flow of water in these rivers to produce electricity cheaply without causing too much environmental damage. Hydroelectric power can remove the latent cost of nuclear power plants because of the need of processing the nuclear waste and fear of environmental contamination in case of tsunamis or accident. Small hydroelectric power projects also do not have any environmental threat as in the case of tsunamis like what happened in Fukushima nuclear power plant. Accidents like Chernobyl and the environmental contamination after the accident can also be avoided in the future.
Mini, Micro and Pico hydroelectricity power plants are under exploited area of electricity generation. There are millions of kilometers of under exploited rivers, including built up rivers and streams in the world as far as hydroelectricity production concerned. Probably exploiting rivers and streams which are flowing through continents then we can produce green energy and reduce the use of petroleum-based products or nuclear power plants for energy generation.